Key summary:
The stock exchange is a market place where buyers and sellers gather to transact. It’s a convenient place for investors to meet buyers and sellers in one place. The stock market, however, is where the transaction of most stocks takes place, but there are still a lot of products in the financial market, such as in London where there is an International Petroleum Exchange specially for the transaction of petrol, or Hong Kong which has a Gold & Silver Exchange especially for precious metals, and New York, which has the Mercantile Exchange which deals with various kinds of commodities including agricultural products and currencies.
Basically, stock is not just a product for a transaction, it is also a certificate to prove the holder owns a number of shares in a company. So when a holder thinks the prospect of that company is promising, he can hold more shares or vice versa. When looking to buy more shares or deciding to sell shares, one has to go to the exchange house to do the transactions. That is why the exchange house exists.
Companies listed in the market have to undergo a series of processes to ensure they are well established and reliable. When these companies are growing and developing well, it’s a positive sign that the general economy of their country of origin is in good shape, which in turn may attract more investors to enter that market. The total value of that share increases, meaning shareholders are better off and can have more funds for development of the company. Additionally, when prospects for the economy are good, it also attracts foreign capital. These days, in a world of globalisation, every city is facing keen competition; every city wants to attract more capital. It’s simple, if the market wants to rise, new capital must be injected into it. When new capital comes in, it can further push the market up and re-attract more – forming a virtuous cycle.
In the mid centuries, the concentration of manpower was quite important regardless of whether it be in war or economic development. Following the Industrial Revolution, machines came into existence – replacing manpower and placing the importance now on technique instead of strength. However, the development of techniques needs capital. Therefore the concentration of capital is the most important factor for a city or country’s development. Nowadays, every city or country aims to develop as a financial centre because of capital concentration. Even if it cannot be an international finance centre, it still wants to be a finance centre for its surrounding population.
The stock market reflects the current situation and prospect of that society’s largest enterprises, blooming when investors look favorably upon a stock and dropping when there’s doom and gloom. It’s believed that the stock market is running ahead of the economy by 6 to 9 months, meaning that when the market rises vigorously, a bloom is expected 6 to 9 months later. On the other hand, if it falls greatly a recession is likely. Thus the Dow Jones Index is known as the thermometer of the US economy as well as the world. Therefore, investors should not neglect the Dow Jones Index, whichever way they decide to invest, whether it’s stocks, gold, silver, currency, bonds, or commodities – it’s a world of globalisation. In turn, investors in US stock markets have to diversify and refer to different markets even if they know that the US leads the world.
a) Global factor – The world economic cycle governs the prosperity of every country, normally when the US is in bloom, other countries follow suit and show a healthy and robust economy, but when the US is in recession, other countries will also be gloomy. This is because the US’s international trade and spending power are the strongest and can affect all other countries. However, this doesn’t work in reverse. When there is a setback in the bloom of any other countries, the effect to the US is quite limited. Therefore, the domestic economic factor of the US is affecting not only the internal situation but the whole world.
b) Regional factor – Sometimes things happening in a confined area can affect that area most and not disrupt any other countries. Such as war in the Middle East, of course, which directly affects the war zone, however the refugees that come as a result can affect the whole of Europe, thus resulting in The United Kingdom’s choice to leave the European Union – BREXIT. The shift of the production chain from China has benefited South-East Asia, South Asia and East Asia. Thus we have to evaluate carefully whether those regional factors only affect that area or extend to nearby zones, and sometimes even develop into global factors.
c) Sector factor – This is where different factors can affect that zone seriously and other zones may have some effect. Such as the development of an aerial engine will lower the cost of airlines and bloom the flying industry and bring up the whole market sometimes because the lower cost will lead to more flying. The development of vaccines would not only bloom medical shares but the entire market. It depends on the market sentiment and whether it’s on technology, industry, or medicine at that particular period, and if not a focus, the effect will be on that sector only but sometimes can affect the whole market. Therefore precise evaluation is needed.
d) Company factor – This is usually individual news which can often extend to the whole of the market, such as the products of Tesla will not only bring up the share of that company but the whole market, or the selling of arms would bloom up that company or all arsenal shares, as well as in news of Apple or Microsoft would bring up that company and very often would extend the effect widely. Therefore abundant information and comprehensive evaluation are needed.
a) Stop-high and stop-low
Each country has its policies in place to face various market fluctuations. In some countries, normally there is a daily limit of stop-high and stop-low. Basically, they are aimed at individual stocks, that is when a stock goes up and down vigorously to a certain level, which was formerly 3%, but later on extend to 5%, that share would stop trading on that day, while other shares can carry on. However, for such a system there are apparent advantages and disadvantages such as:
Advantages
i. Protect the interest of investors and limit their daily losses.
ii. Limit the control of the big shots.
iii. Give cool down time for investors.
iv. Buy time to digest unfavorable news.
v. Awaiting further good news.
vi. Watch the response of the markets and wait for a response.
vii. Give investors time to gather more funds and news.
Disadvantages.
i. Against free economy.
ii. Investors may miss the chance to cut their losses.
iii. When transactions are hindered, thus cannot attract foreign capital.
iv. Insufficient time for response to slow investors.
v. Prolonging the bear market.
vi. Capital cannot flow in and out easily.
vii. Smart investors cannot earn as much as they can.
b) Circuit breaker
This is a tool mainly aimed at the sudden crash of the stock market as a whole and can be said to be in one direction only, not as stop-high or stop-low having both directions. It is aimed at the whole market rather than individual stocks. A circuit breaker actually is a by-product of the crash of 1987.
President Ronald Reagan introduced Reaganomics and led to a bloom in the stock market for several years. The 1987 October stock crash came out of the blue without any omen. The market rose steadily, but investors put on stop loss at different levels to lower the risk. This was the first time where the computerised stop loss was introduced. When touching the first level, a lot of sellers came out automatically to bring down the price and again, the slump brought about another new slump. After that, they introduced the Circuit Breaker not to allow such a great fall to happen again.
In order to reduce market volatility and massive panic sell-offs, a Circuit Breaker gives traders time to reconsider their transactions. It stops the trading for a short time to allow accurate information to flow among market makers and institutional traders to assess their positions and make rational decisions.
The calculation of a Circuit Breaker is based upon the S&P 500, for it is more comprehensive. It is divided into 3 levels. Level 1 is set at 7% of the fall, and level 2 at 13%. Both have 15 minutes to stop trading time and let everyone cool down. Level 3 is set at 20%, and trading will be stopping for the remainder of that day. The term circuit breaker means to borrow from a supply of electricity when wires are overheating – the fuse stops the supply. Therefore, it can be described as a preventative, protective tool.
Ten years after the crash of October 1987, a Circuit Breaker was first used in the October crash in 1997, which brought about a saying that the US stock would drop greatly every October, or will have a crash in XXX7 years, but of course, both are untrue.
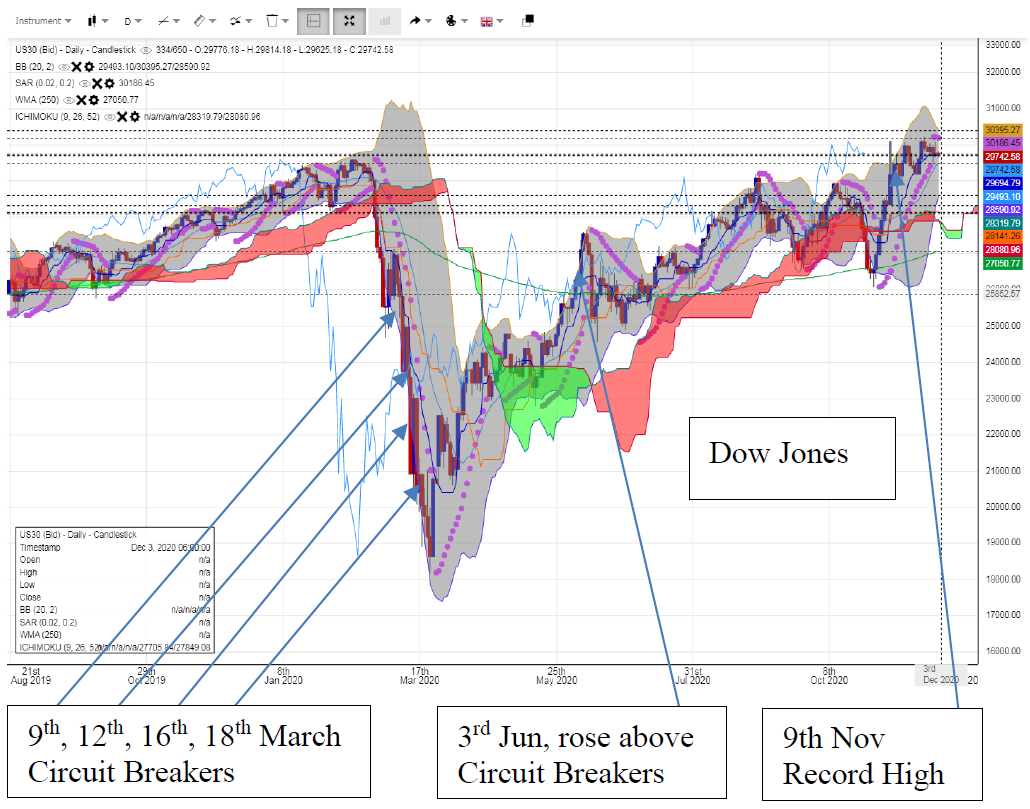
A Circuit Breaker had to be used again in 2020 due to Coronavirus on 9th, 12th, 16th, 18th March for four days, but luckily had a V-shape rebound.
The underneath chart shows the 4 Circuit Breakers of Dow Jones, the fourth day (18th March) shown an anti-falling hammer, and several days later, a vigorous V-shape rebound started. On 3rd June, it rose above the first day of Circuit Breaker (9th March), meaning total recovery. On 9th November it broke a record high, which is clear to see in the chart analysis.
c) Short selling
Normally people buy in a stock and wait for a higher price to sell out, in order to make it more flexible, short selling is allowed. When one expects the market to fall, one can sell without any stocks in hand and buy back at a lower price to make a profit. In many emerging economies, they prohibit short selling, but in the US it is legal. However, the Securities Commission leaves the decision to each brokerage to implement. That means the firm has the right to ask the client to pay a certain amount of deposit first before starting and short selling, in case they are unable to fill the loss. Some even ask the client to borrow the stocks and pay a certain amount in borrowing fees. These are all commercial decisions. However, there are still some advantages and disadvantages as follows:
Advantages
i. More flexible, can do the transaction at any time, no need to wait for the market to rise.
ii. Avoid the strike of bad news.
iii. Make the market more stable, why the market sometimes would collapse greatly, because it rises continuously without any blockages, and when short selling is allowed, it will not be allowed to go out of control in a bull market, therefore the collapse will be lessened. When the bear market returns, because some short selling would have already been done on the high, as it falls, those selling short will take profit which can stop the fall to a certain extent.
Disadvantages
i. May lead to panic selling when the market collapses.
ii. Normally, people like to see the prices go up no matter in what market else, it would bring about psychological diseases when too many people are going for short selling.
iii. Short sellers may not be welcomed by traditional investors who consider them trouble makers. This would bring disharmony.
There are 5 major indices in the US stock market. The three more famous ones are the Dow Jones, S&P and the NASDAQ, with two further lesser known indexes such as the Russell and the Wilshire. The introduction of a stock index is to give investors a guideline to the market. Before indices, people would just put an eye on several major stocks and use them to guide the whole market. However, due to different company policies and situations, there comes a symptom of one stock going up and the other going down, so it’s not easy to evaluate. Therefore an index is needed to tell the general situation of the market. As a rule, investors usually gain access to a group of important shares as part of an index. Some might ask why they don’t include all shares of the market to compose the index. The answer is quite simple, for there are a lot of small and unimportant shares in the market which has few transactions, if we put them into calculation it would not reflect the actual situation and may have some bias. Because they are not from the major trend and sometimes do not follow the major trend, their prices may be extremely high or low due to their individual effect, so they cannot reflect the actual situation of the market. Thus some should be eliminated from the component of the index. Actually, some markets do have such a kind of index, but this is not welcomed.
For example, Hong Kong has two indices. The first one is the famous Hang Seng Index established by a think tank of Hang Seng Bank in 1964. At first, it consisted of 33 member stocks but later grew to 55 members. Now it represents about 63% of the market components and is considered a representative of the market. In the 1960s, there were 4 stock exchanges in HK and 3 of them had their individual index. Hang Seng Index was the index of Hong Kong Club where most traders are of foreign capital. In 1986, four exchanges combined to form one, the Hang Seng Index kept on running while the other two stopped. Another new index came into existence known as the All Ordinary Index. It is based on every single stock of the market. Even though the basic theory is quite ideal for including every share, practically those small shares only have rare transactions, but prices are quite high or low running off the primary trend. Therefore, such an index is always neglected and considered inaccurate.
In Australia, they have an index bearing a similar name known as the All Ordinary Share Index, but it is just a standard index using 500 member components and not as Hong Kong using every single share. In London, they also have the FTSE All share Index which includes every single share, however, this is mostly neglected, compared to the favoured FTSE 100 or just FTSE. This shows that the concept of an ‘all share’ does not work, and all major markets have decided to pick a number of important shares to calculate their index. Nevertheless, these indices need to be evaluated every 5 to 10 years, and their components chanced to reflect the current market situation.
a) Dow Jones Index
Dow Jones is practically the most crucial index in the world. It was invented by two editors of the Wall Street Journal – Charles Dow and Edward Jones, hence bearing their last names. The first index was introduced in 1884 as Dow Jones Transportation Average, mainly on railway and shipping shares, for at that time they believed a sound transportation system could grow the economy of a society. In 1885 there came the Dow Jones Average (DJA) mainly on industrial shares because it was the time just after the Second Industrial Revolution, and industry becomes the main structure of society. In 1896, it was renamed Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) and the name is used today. Later on, they developed into Dow Jones Composite and Dow Jones Finance, but DJIA is still treated as the main index and not just part of the Dow Jones System. It is composed of 30 major industrial stocks and thus many other indices have followed suit and launched carrying 30 stocks. However, as the market grew, some have added more components while others remain unchanged. After the “Dot Com Bubble” of the 1990s, the components of DJIA changed greatly, for everyone knew that it’s a world of information and technology. So can an index of industrial product represent everything? Surely no. Therefore, the components changed only five to six are concerning industry, and over half are concerning information and technology while the rest are from various sectors. Therefore nowadays, people would like to call the index the Dow Jones or Dow instead of DJIA, for its previous name no longer seems relevant. But the importance is still the same.
The calculation of DJIA is based upon the following formula of arithmetic mean:
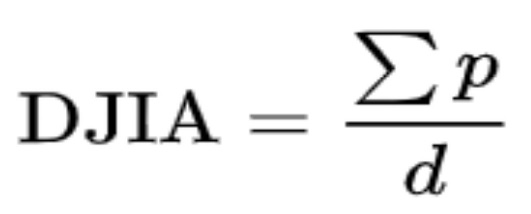
Where p are the prices of the component stocks and d is the Dow Divisor.
Make it down to earth, let’s compare with the Hang Seng Index of Hong Kong under the same market situation but with different formulas. Let’s assume there are only 3 stocks in the market and see what happens on the next day when using the Hang Seng Index and Dow Jones Index formula. Of course, both of them start with 100 as the base point.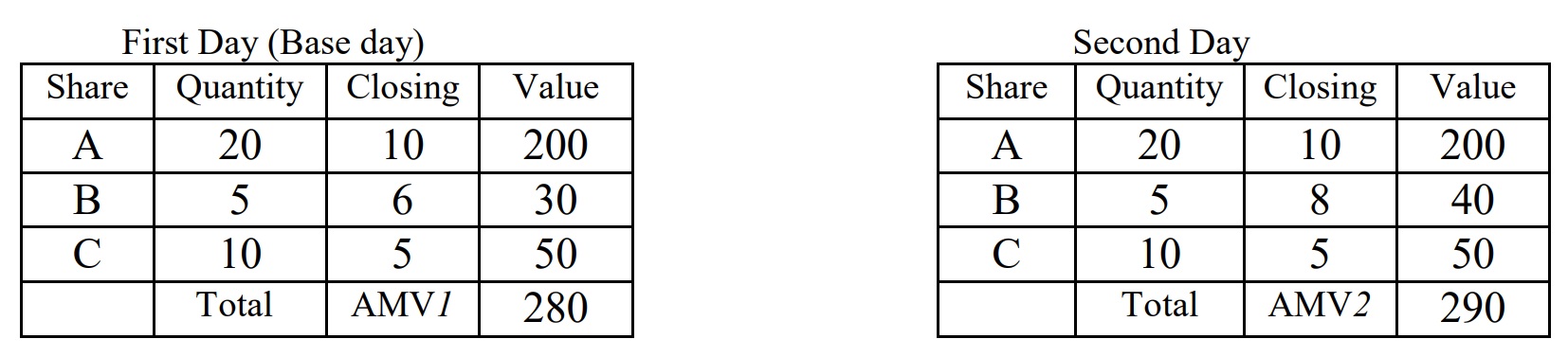
Formula of Hang Seng Index
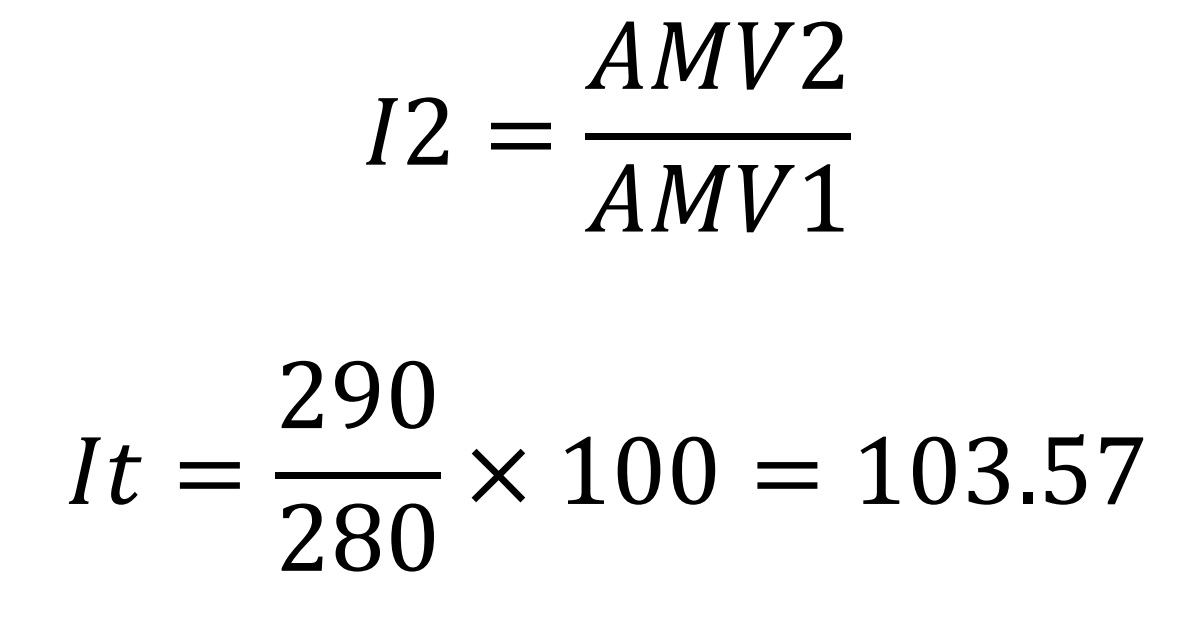
(I means Index and t means the day of calculation)
Formula of Dow Jones
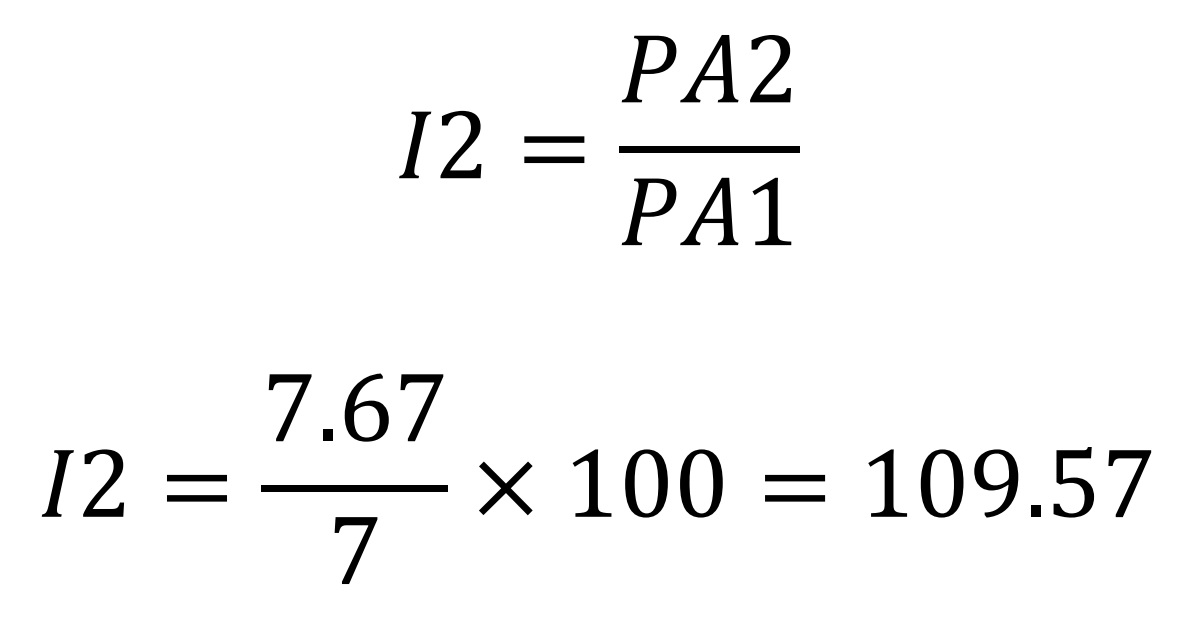
(PA means price average, AMV is average mean value)
First Day (10 + 6 + 5)/3 = 7;
Second Day (10 + 8 + 5)/3 = 7.67
Therefore, under the same market situation, the fluctuation of Dow Jones is larger than that of Hang Seng Index. That is why speculators like to use Dow Jones formula as an index. It denotes great vitality. When the market goes up and down vigorously, they can have more profit no matter buying or selling, especially in the index future. In contrast, the Hang Seng Index is more stable and is suitable for another group of investors.
b) Standard and Poor
The name of Standard and Poor always aroused some misunderstanding, some people may think of the living standard of poor people or normal people. But actually not. The name was derived similarly to that of the Dow Jones – it came from the family names of Mr. Standard and Mr. Poor. But don’t be fooled, this Mr. Poor is very rich, not poor at all. He should be amongst the top 500 wealthiest people in the world. He indeed is “the richest Poor”.
Speculators welcome the Dow Jones, but S&P usually is for government institutions to make their policies or think tanks to do their research. For they have 3 major indices and were established in 1957.
S&P 500 is the main index, when appearing in media without pointing to which section, “S&P” means typically “S&P 500”. It is a joint venture of S&P and Dow Jones. In order to make the index more comprehensive, the component members increased to 500 large enterprises. S&P 400 is for medium enterprises and S&P 600 for small enterprises, S&P 1500 is a total of all. To sum up is:
S&P 400 Medium enterprise
S&P 500 Large enterprise (main index)
S&P 600 Small enterprise
S&P 1500 Composite (the sum of previous 3)
c) NASDAQ
NASDAQ means “National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations”. Actually, the name has nothing to deal with information and technology even people describe it as an IT Index. It was established in 1971 and the first market to use electronic quotation and dealing instead of open outcry in the New York Stock Exchange. Thus, it attracted a lot of new technology companies, especially those from Silicon Valley, for those companies are on the stage of maturity after 20 years’ development. The original idea was to let new companies listed in NASDAQ market first and when they are matured they can move to NYSE. But there was a famous company known as International Business Machines (IBM) they do not want to move, and thus all other new technology enterprises decided to stay and formed a market of technology companies. In 1998 it became the first exchange in the world to use online trading. The market capitalization of NASDAQ in 2019 is US$11.1 Trillion and for NYSE is US$28.5 Trillion, always about 40% of the latter. It is sometimes known as “NASDAQ 100”, for it uses 100 components to calculate the index.
d) Russell 1000
Russell Index is divided into Russell 3000 and Russell 2000, it is own by the FTSE of London but aims at the New York Stock market only. It was established in 1984, Russell 3000 covers 98% of the market capitalisation, still 2% are out of the range for too small and insignificant and should not enter to interfere the whole index, or else it will be inaccurate. The Russell 2000 is much more used; components are simply on the top 2000 of the Russell 3000.
e) Wilshire 5000
This is the most advance and modified index established in 1974. It can have a broader coverage of 5000 components but still would not be affected by smaller firms. That means they are using a market capitalisation weighted index. They calculate both large and small firms up to 5000 to broaden the scope as far as can be, but in order to avoid unnecessary noise, they would use larger ratio times the large companies and smaller ratio times the smaller companies. The Index of Taiwan is directly called Weighted Index, for they want to let people know they are using such an advanced formula.
The formula of Wilshire is
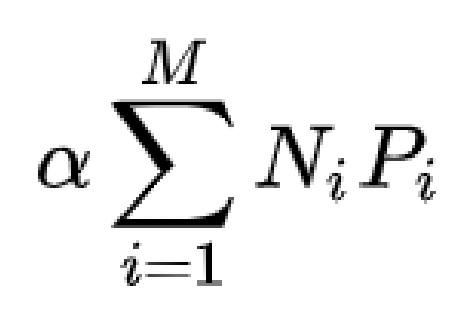
M = Number of issues included in the index;
Pi = Price of one share of issue i included in the index;
Ni = Number of shares of issue i for the full capitalization version, or the float of issue i for the float-adjusted version;
α = a fixed scaling factor.
Actually, it is seldom used because people are accustomed to the Big Three.
To sum up, Dow Jones is for individual investors, speculators and reference of other countries. S&P is for government institutions and think tanks, while NASDAQ shows shares excluding the financial sector. Stock markets are running six to nine months ahead of the economy, but still have to cope with practical situations. In 2017, the Dow Jones made record high 71 times, every 3 to 4 transaction days would have one record high on average. Therefore, the world economy was in big bloom in 2018. However, in August 2019, the S&P established the longest bull market in US history from the Financial Tsunami until then. But in early 2020, there came the Coronavirus and soon brought about the Circuit Breaker. The world economy in the second season was in disaster. Luckily with the sound background of the longest bull market, a V-shape rebound occurred and recovery was observed clearly in the third season.
When buying stocks, there is sometimes a symptom that the stocks do not follow the trend of the index and upset people. Of course, if the index goes down and that individual stock goes up, investors will be very happy; but on the other hand, if the index goes up and that stock down due to individual company policy or situation will go down, such as some Chinese stocks sanctioned by the US state department, investors will be annoyed. To make sure everything goes in accordance with the index all the time, the only way is to invest in the index. That is Index Future is a commodity, you are buying the uptrend or downtrend of the index. In the Index Future, short selling is widespread. The main functions of stock futures are:
a) Future is an indication of the market, when the future is at a higher level than the original index, which means most people have good prospects on the market and when it is lower than the original index, the prospect is not so good. Therefore it can be said as an indication of the future trend.
b) Use as an arbitrage. When a big shot is buying in a large amount of stocks, but afraid in the future there may be some unfavorable factor that would make the stock go down and the main point is not a hundred percent sure, may happen or may not happen. In such a case, he can sell the future as arbitrage. Because the timing and liquation of the stock and future may not be the same, so the difference will be the profit or the money that lessens the risk.
c) Accelerate the time of entering and leaving the market. Typically, when a big investor wishes to buy the stock, since his amount is quite extensive and may buy up the price, they buy little by little, day by day or week by week. Sometimes they release certain amounts to lower the price. We discuss this further later on in our chart analysis. It may take several months to finish such bulk buying. In order to save time, he can buy the future first and even if he buys quickly and the stock price is thus pushed up, he still can get profit from the future to cover the expensive cost of the stock. Therefore he can finish the total buying in a shorter time.
d) Can have bigger profit than buying original stocks. Normally one point of the future would have a greater profit than the stock, and if using leverage system the capital needed is smaller, therefore he can buy more lots and have a greater profit using the same amount of capital.
e) In Hong Kong, it can be used to maintain the pegged currency rate of Hong Kong Dollar since it is fixed at the rate of one US dollar to roughly 7.8 Hong Kong Dollars. In 1998, the Asian Financial Crisis started in Thailand and later George Soros attacked Hong Kong. He attacked the Hang Seng Index Future and the Treasury of Hong Kong defended the Hong Kong Dollar both in the future market and the concrete stock market of Hong Kong. George Soros met his Waterloo in Hong Kong and thus the Asian Financial Crisis ended. The Hong Kong Dollar was protected by the battle of Hang Seng Index Future.
The US market doesn’t have a lunch break and just runs continuously (see times below). Asia, on the other hand, normally has one-hour lunch breaks or more. In Bangkok, Thailand, they have a lunch break of two hours. In Jakarta, Indonesia, their lunch hour on Friday is two and a half hours, the longest amongst all exchanges. In Taiwan, their trading hour is from 9:00 am to 1:30 pm, no lunch break but the whole afternoon is used for settlement. In Tel Aviv, Israel, the standard workweek is from Sunday through Thursday. Friday is a short workday and Saturday is a weekend vacation day. The exchange is open on Sundays but closes on Fridays and Saturdays, however, should anything happen on Friday, they will reflect trading before the western market opens on Monday. In Frankfurt, their trading hour is from 8:00 am to 8:00 pm but in Eschborn of Germany, the Eurex Exchange opens from 8:00 am to 10:00 pm, the longest among all exchanges. The US trading hours and holidays are as follows:
| Opening Hours | Extended Hours | |
| Eastern Time (EST) | 9:30 a.m. – 4:00 p.m. | 04:00 a.m. – 8:00 p.m. |
| Central Time (CST) | 8:30 a.m. – 3:00 p.m. | 03:00 a.m. – 7:00 p.m. |
| Mountain Time (MST) | 7:30 a.m. – 2:00 p.m | 02:00 a.m. – 6:00 p.m. |
| Pacific Time (PST) | 6:30 a.m. – 1:00 p.m. | 01:00 a.m. – 5:00 p.m. |
NYCETape A Pre-Opening Session 6:30 a.m. ET
Core Trading Session: 9:30 a.m. to 4:00 p.m. ET
TAPE B & C Pre-Opening Session 6:30 a.m. ET
Early Trading Session: 7:00 a.m. to 9:30 a.m. ET Core Trading Session: 9:30 a.m. to 4:00 p.m. ET | NYCE American Equities
Pre-Opening Session 6:30 a.m.
Early Trading Session: 7:00 a.m. to 9:30 a.m. ET
Core Trading Session: 9:30 a.m. to 4:00 p.m. ET
Late Trading Session: 4:00 p.m. to 8:00 p.m. ET |
The Nasdaq Stock Market sessions, with times in the Eastern Time Zone are:
The Nasdaq Stock Market averages about 253 trading days year.
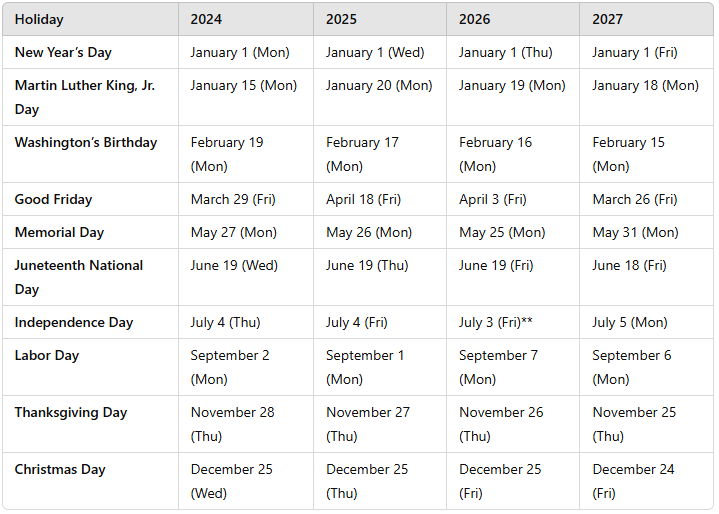
Notes:
Markets close early at 1:00 PM Eastern on:
Nota Bene